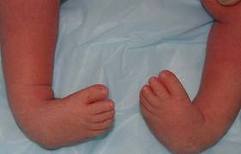
Congenital Talipes Equino Varus
1. Definition

Talipes = talus and pes/foot
Equino = Foot like horse (plantar flexi) position
Varus = heel varus, a decrease of the leg-foot angle
CTEV is a congenital deformity of one foot or both with description same as its abbreviation.
In Ad Equate = Inversion at subtalar joint, Adduction of tanonaviculare joint, Equino of ankle joint
2. Incidence
a. 1-2 in 1000 live births
b. Half the cases are bilateral
c. Boys are twice than girls
d. 10 % genetic factor and an initial mutation in the family tree
e. 1:4 chance probability for child who has one parent and one older sibling got clubfoot.
3. Etiology
Polygenic and multifactorial (speculation):
a. abnormal intrauterine forces
b. arrested fetal development
c. abnormal inserted muscle and tendon
d. abnormal rotation of talus in the mortise
e. germ plasm defects
4. Pathogenesis and pathology
a. Associated deformities are caused by shortened/contracted muscles, joint capsules, ligaments, and fascia.
b. Congenital dislocation (tallo, calcaneo, navicular joint)
c. Change of bone shape
d. The fibrous capsules of all the deformed joints are thick and contracted on concave side of the deformity. (contracture of soft tissue and congenital atresia)
5. Clinical features and diagnosis
a. General examination :
1) Other abnormalities : spina bifida, amyloplasia congenita
2) Syndrome Clubfoot : Larsen’s Syndrome, amniotic band syndrome
b. Characteristic examination :
1) Fore foot : adductus and supination
2) Hind foot : Equinus and varus
3) Tallar neck deformity : medial and plantar deviation
4) Calcaneus : medial rotation
5) Naviculare and cuboid : medial displacement
c. Radiographic diagnosis (for assessment of therapy progress as well)
1) From dorsoflexion lateral view : talocalcaneal angle < 35
2). From Anteroposterior view
a) Talocalcaneal angle <20 (normal 20-40)
b) Talo-first metatarsal angle negative ( normal 0-20)
3) Parallelism tallus-calcaneus is seen on both views
6. Treatment
a. Non surgery
Ponseti Method : < 6 months old
1) Serial (weekly) long leg plaster casts (6 weeks)
a) Correction of the cavus by aligning the first ray with remaining metatarsal
b) Lateral pressure on the distal talar head as a fulcrum to correct the fore foot adduction and heelvarus.
c) All deformities are correct gradually
2) Cast until there is about 60 degrees of external rotation (about 4-6 casts)
3) Percutaneous tendo Achilles tenotomy in cast room under local anesthesia, followed by final cast (3 weeks)
4) After final cast removal, apply Normal last shoes with Denis Browne bar set at 70 degrees external rotation (40 degrees on normal side)
5) Denis Browne splint full time for two months, then night time only for two-four years.
b. Surgery
1) 6-9 months. Surgical soft tissue release with tendon lengthening (be carefull with posterior tibial artery and dorsalis pedis artery)
2) 3-10 years. Medial opening or lateral column-shortening osteotomy or cuboideal osteotomy
3) 8-10 years. Triple arthrodesis is the only procedure possible to elaminating pain and deformity. Talectomy for insensate feet.
7. Prognosis
Depend on the age that the manipulation begin
The Ponseti method, if correctly done, is successful in >95% cases.
8. Complication
a. Contracted soft tissue fail to grow adequately in length produce limited production
b. Recurrence deformity (particularly during rapid skeletal growth period)
c. Complication of treatment : pressure necrosis of joint cartilage
Read Full Post | Make a Comment ( None so far )